职责链模式
职责链模式: 类似多米诺骨牌, 通过请求第一个条件, 会持续执行后续的条件, 直到返回结果为止。
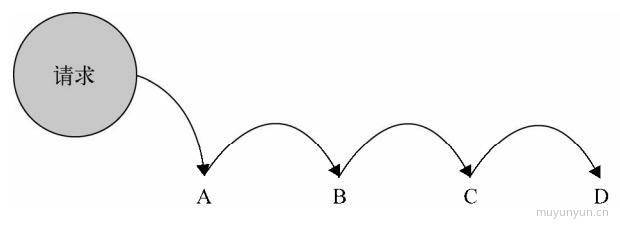
重要性: 4 星, 在项目中能对 if-else 语句进行优化
场景 demo
场景: 某电商针对已付过定金的用户有优惠政策, 在正式购买后, 已经支付过 500 元定金的用户会收到 100 元的优惠券, 200 元定金的用户可以收到 50 元优惠券, 没有支付过定金的用户只能正常购买。
// orderType: 表示订单类型, 1: 500 元定金用户;2: 200 元定金用户;3: 普通购买用户// pay: 表示用户是否已经支付定金, true: 已支付;false: 未支付// stock: 表示当前用于普通购买的手机库存数量, 已支付过定金的用户不受此限制const order = function( orderType, pay, stock ) {if ( orderType === 1 ) {if ( pay === true ) {console.log('500 元定金预购, 得到 100 元优惠券')} else {if (stock > 0) {console.log('普通购买, 无优惠券')} else {console.log('库存不够, 无法购买')}}} else if ( orderType === 2 ) {if ( pay === true ) {console.log('200 元定金预购, 得到 50 元优惠券')} else {if (stock > 0) {console.log('普通购买, 无优惠券')} else {console.log('库存不够, 无法购买')}}} else if ( orderType === 3 ) {if (stock > 0) {console.log('普通购买, 无优惠券')} else {console.log('库存不够, 无法购买')}}}order( 3, true, 500 ) // 普通购买, 无优惠券
下面用职责链模式改造代码:
const order500 = function(orderType, pay, stock) {if ( orderType === 1 && pay === true ) {console.log('500 元定金预购, 得到 100 元优惠券')} else {order200(orderType, pay, stock)}}const order200 = function(orderType, pay, stock) {if ( orderType === 2 && pay === true ) {console.log('200 元定金预购, 得到 50 元优惠券')} else {orderCommon(orderType, pay, stock)}}const orderCommon = function(orderType, pay, stock) {if ((orderType === 3 || !pay) && stock > 0) {console.log('普通购买, 无优惠券')} else {console.log('库存不够, 无法购买')}}order500(3, true, 500) // 普通购买, 无优惠券
改造后可以发现代码相对清晰了, 但是链路代码和业务代码依然耦合在一起, 进一步优化:
// 业务代码const order500 = function(orderType, pay, stock) {if ( orderType === 1 && pay === true ) {console.log('500 元定金预购, 得到 100 元优惠券')} else {return 'nextSuccess'}}const order200 = function(orderType, pay, stock) {if ( orderType === 2 && pay === true ) {console.log('200 元定金预购, 得到 50 元优惠券')} else {return 'nextSuccess'}}const orderCommon = function(orderType, pay, stock) {if ((orderType === 3 || !pay) && stock > 0) {console.log('普通购买, 无优惠券')} else {console.log('库存不够, 无法购买')}}// 链路代码const chain = function(fn) {this.fn = fnthis.sucessor = null}chain.prototype.setNext = function(sucessor) {this.sucessor = sucessor}chain.prototype.init = function() {const result = this.fn.apply(this, arguments)if (result === 'nextSuccess') {this.sucessor.init.apply(this.sucessor, arguments)}}const order500New = new chain(order500)const order200New = new chain(order200)const orderCommonNew = new chain(orderCommon)order500New.setNext(order200New)order200New.setNext(orderCommonNew)order500New.init( 3, true, 500 ) // 普通购买, 无优惠券
重构后, 链路代码和业务代码彻底地分离。假如未来需要新增 order300, 那只需新增与其相关的函数而不必改动原有业务代码。
另外结合 AOP 还能简化上述链路代码:
// 业务代码const order500 = function(orderType, pay, stock) {if ( orderType === 1 && pay === true ) {console.log('500 元定金预购, 得到 100 元优惠券')} else {return 'nextSuccess'}}const order200 = function(orderType, pay, stock) {if ( orderType === 2 && pay === true ) {console.log('200 元定金预购, 得到 50 元优惠券')} else {return 'nextSuccess'}}const orderCommon = function(orderType, pay, stock) {if ((orderType === 3 || !pay) && stock > 0) {console.log('普通购买, 无优惠券')} else {console.log('库存不够, 无法购买')}}// 链路代码Function.prototype.after = function(fn) {const self = thisreturn function() {const result = self.apply(self, arguments)if (result === 'nextSuccess') {return fn.apply(self, arguments) // 这里 return 别忘记了~}}}const order = order500.after(order200).after(orderCommon)order( 3, true, 500 ) // 普通购买, 无优惠券
职责链模式比较重要, 项目中能用到它的地方会有很多, 用上它能解耦 1 个请求对象和 n 个目标对象的关系。